Cationic Polyacrylamide Emulsion Flocculant
Brand Jiufang
Product origin Shenyang
Delivery time Lead time: 7days
Supply capacity 2000Metric Tons per Month
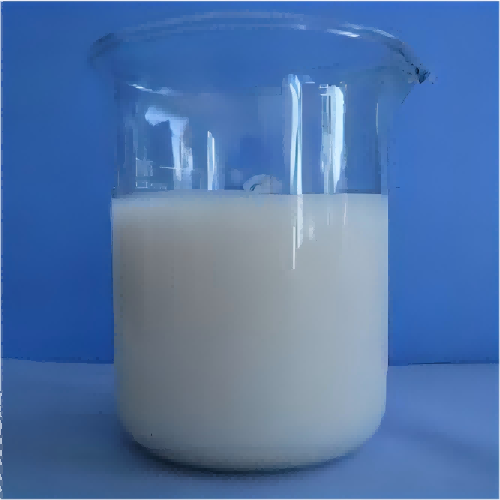
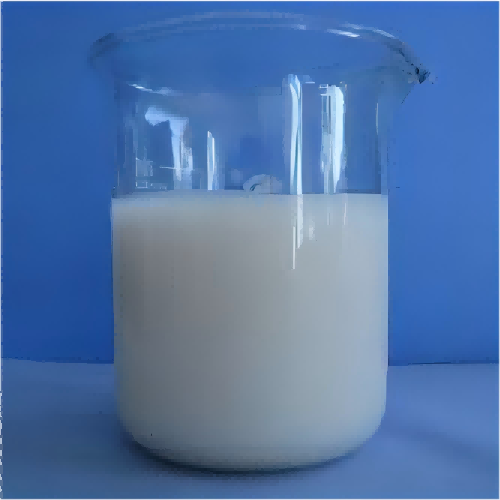
1.Polymer polyacrylamide cationic (chemical PAM emulsion) is a type of chemical polyacrylamide flocculant which is a milky emulsion.
2.Cationic liquid flocculant is made through DMC being copolymerized with white oil.
3. Using the special dissolve device to dissolve the chemical polyacrylamide flocculant is the best way for the polymer polyacrylamide cationic.
Download
Cationic polyacrylamide emulsion flocculant is a kind of polymer product with wide applications.
1) Good water solubility: Cationic liquid flocculant can dissolve rapidly in water to form a uniform solution.
2) Cationic property: Chemical PAM emulsion has positive charges and can have a strong interaction with substances with negative charges.
3) Emulsion state: Polymer polyacrylamide cationic is in a liquid emulsion form, convenient to use and easy to disperse and mix.
4) Efficient flocculation: Chemical polyacrylamide flocculant has a good flocculation effect on suspended solids and organic matters in sewage and can quickly form larger flocs to accelerate precipitation.
Determining the dosage of cationic polyacrylamide emulsion flocculant requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors.
The following are some methods and steps:
1. Experimental testing Prepare solutions of cationic polyacrylamide emulsion flocculant with different concentrations. You can start from a lower concentration and gradually increase concentration of polymer polyacrylamide cationic. For example, set several concentration gradients of cationic liquid flocculant, such as 0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3%, etc. Take a certain amount of water samples or sludge samples to be treated. Water samples can be actual industrial wastewater, domestic sewage, etc.; sludge samples can be obtained from sewage treatment plants or related places where sludge is generated. Add different concentrations of cationic polyacrylamide emulsion flocculant solutions to different water samples or sludge samples respectively and stir well to ensure the full mixing of the reagent and the treated object. And then observe the coagulation of suspended solids in the water sample and the dehydration effect of the sludge after adding the chemical PAM emulsion. The flocculation effect can be preliminarily judged by observing indicators such as the size of the flocs and the sedimentation speed with the naked eye. For water samples, changes in parameters such as turbidity, suspended solids content and chemical oxygen demand (COD) can be measured; for sludge samples, indicators such as the moisture content of the sludge can be measured.Determine the optimal dosage range based on the experimental results. Generally, the corresponding dosage range when the flocculation effect is good and the water quality parameters improve significantly is the preliminarily determined optimal dosage range.
2. Consider the characteristics of the treated object when using chemical polyacrylamide flocculant. 1) Water quality characteristics: The types and sources of wastewater are different and their water quality characteristics will also vary greatly. For example, industrial wastewater may contain high concentrations of organic matter, heavy metals, etc., while domestic sewage contains more suspended solids and organic matter. The pH value of the wastewater will also affect the dosage of cationic polyacrylamide emulsion flocculant. Generally, the effect of the reagent is better under neutral or near-neutral pH conditions. If the pH value of the wastewater is too high or too low, the dosage may need to be adjusted or pretreatment may be required. Parameters such as the suspended solids content and turbidity of the wastewater will also affect the dosage. Wastewater with a high suspended solids content and high turbidity usually requires a larger dosage.
2) Sludge characteristics: The types and sources of sludge are different and their properties will also be different. For example, biochemical sludge, chemical sludge, etc have differences in moisture content, particle size, and organic matter content. The moisture content of the sludge is one of the important factors in determining the dosage. Sludge with a high moisture content requires a larger dosage to achieve a better dehydration effect. The particle size of the sludge will also affect the dosage. Sludge with smaller particles requires more reagents to promote flocculation and dehydration.
3. Refer to empirical data and manufacturer's recommendations
1) Empirical data: You can refer to empirical dosage data under similar treatment processes and water quality conditions. These data can be obtained from relevant industry literature, technical manuals, engineering cases and other channels.
2) Manufacturer's recommendations: The manufacturer of cationic liquid flocculant usually provides some dosage recommendations based on the characteristics and application scope of the product. When determining the dosage, you can refer to the manufacturer's recommendations and adjust them according to the actual situation.
4. On-site adjustment In practical applications, add the dosage of polymer polyacrylamide cationic according to the preliminarily determined dosage range and closely observe the treatment effect. If the flocculation effect is not ideal or the dehydration effect is poor, the dosage of chemical PAM emulsion can be appropriately adjusted. The method of gradually increasing or decreasing the dosage of chemical PAM emulsion can be used to observe the changes in the treatment effect to determine the optimal dosage of chemical PAM emulsion. At the same time, comprehensive judgment can also be made by combining water quality monitoring data and sludge dehydration effect and other indicators. During the process of adjusting the dosage, it is necessary to record the changes in the dosage and the treatment effect to provide a reference for subsequent adjustments. In conclusion, determining the dosage of cationic liquid flocculant requires multiple steps such as experimental testing, considering the characteristics of the treated object, referring to empirical data and manufacturer's recommendations and on-site adjustment and comprehensive consideration of various factors to achieve the best treatment effect and economic benefits.
Industry-specific attributes:
| Name | Cationic liquid flocculant | |||
| Chemical Formula | (C3H5NO)n | |||
| CAS NO. | 9003-05-8 | |||
Other Attributes:
| Appearance | Chemical PAM emulsion | |||
| Activate Content | 48% | |||
| Viscosity Range(ml/g) | 1200~1600 | |||
| Residue | 0.12% | |||
| Insoluble Substance(%) | 0.1 | |||
| Cationic Charge | 80% | |||
| Dissolving Time,min | 40 | |||
| Storage Temperature,℃ | 0~35 | |||
| Shelf Life,month | 12 | |||
Supply Ability:
| Supply Ability | 2000Metric Tons per Month | |||
Lead Time:
| Quantity(kilograms) | 1~50 | >50 | |
| Lead Time(days) | 7 | negotiated | |














